- New Products
- Brake Caliper Stud Kits
- AP Racing Big Brake Kits
- AP Racing Brake Discs
- AP Racing Brake Calipers
- AP Racing Master Cylinders
- Essex Brake Bundles (upgraded pads, lines, fluid, discs that work with OEM Calipers)
- Brake Pads
- Brake Fluids
- Spiegler Brake Lines
- Tools, Temperature Indication and Protection Products
- Wheels
- Suspension
- Versodeck Flooring
- Apparel and Merchandise
- Formula SAE
- Clearance
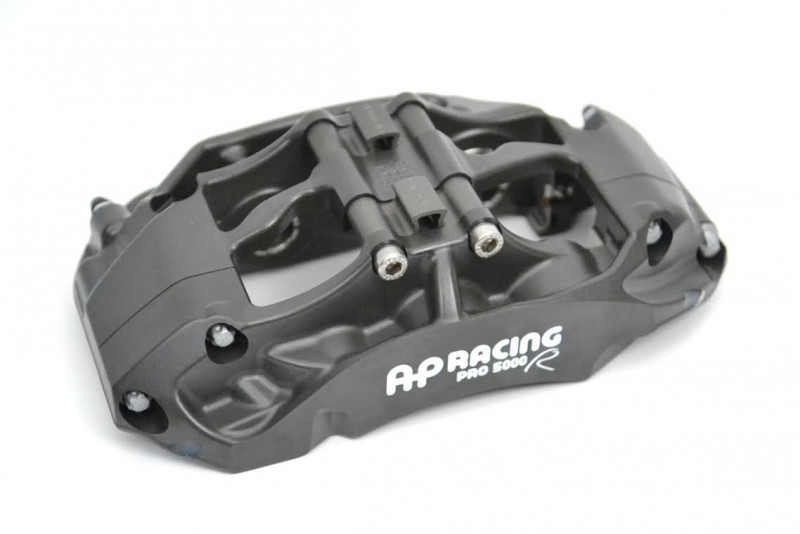
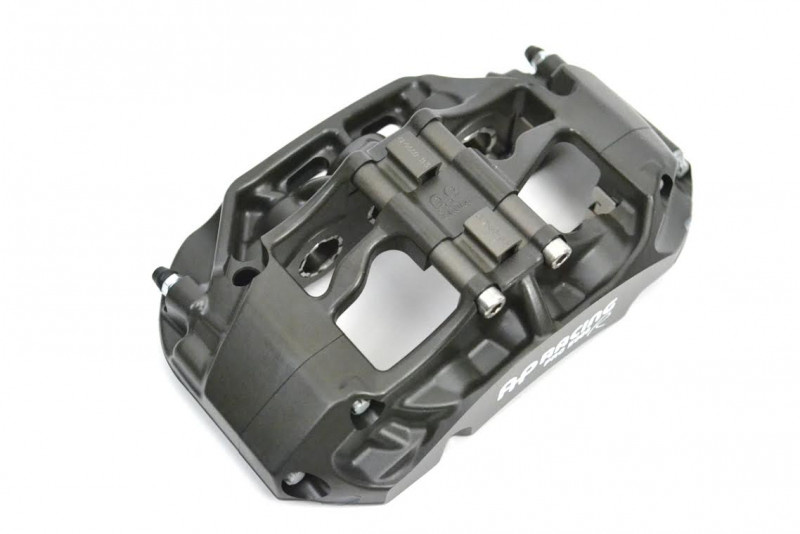
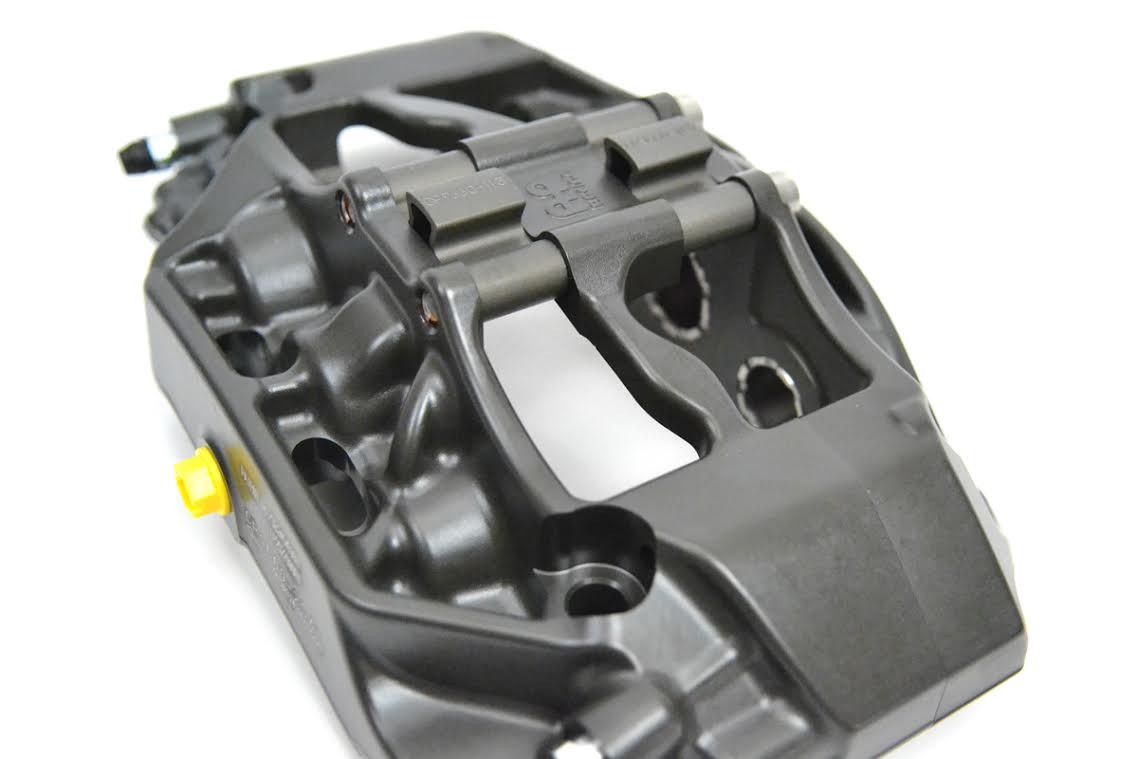
CP9660-2S4L AP Racing Pro5000R Radi-CAL Six Piston (Right Hand, Trailing, Anodized)
Part #: 13.05.20032
Brand: AP Racing
- Anodized aluminum 6-piston Pro5000R Radi-CAL racing caliper
- Stainless Steel, domed-back, ventilated pistons with 4 lb. AKB springs & high temp seals
- Pistons=27mmx2, 31.8mmx2, 38.1mmx2
- 6.2lbs. without pads
- Fits discs 355-380mm x 32-36mm
Show All vehicles this product fits
Application: Track

Radi-CAL
“Radi-CAL” is a blanket term used to describe AP Racing’s patented asymmetrical brake caliper design. Radi-Cal technology is grounded in Computer Aided Design (CAD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA), and allows for organic, alien-looking designs that are a radical departure from conventional caliper designs of the past. Radi-CAL's are widely considered the pinnacle of current brake caliper technology. Since their inception in 2007, these revolutionary calipers have amassed a lengthy string of race victories at all levels of professional motorsport, while redefining brake performance expectations. For more details on the design concept and what these calipers have achieved in professional racing, please visit our blog and read The AP Racing Radi-CAL Story.
The key benefits of the Radi-CAL design:
- Massive Stiffness Increase- A 30+ % increase in both static and dynamic stiffness vs. conventional calipers allows for far less deflection under load, which means superior pedal feel & modulation, more even pad wear, and longer caliper service life.
- Considerable Mass Reduction- Removing all extraneous caliper mass lowers the caliper weight, despite the huge stiffness increases.
- Optimized Airflow- Air moves around and through the caliper more efficiently, providing superior heat evacuation and cooling.
- Efficient Packaging- The asymmetric caliper profile and internal fluid porting allows the caliper to fit into tighter spaces.
CP9660 Pro5000R, The Everyman Radi-CAL

It has taken eight years, numerous generations of the design concept, and advancements in manufacturing techniques, but the Radi-CAL has finally evolved into a viable solution for racers and enthusiasts of all levels and budgets. While many products are supposedly born in racing, there can be no doubt about the Pro5000R pedigree. These calipers are direct descendants of the current crop of F1 and Sprint Cup calipers. They don't look ordinary, because they're not ordinary. They're the epitome of pure racing design: elegant, sparse, and brutally effective. And while they embody and employ the Radi-CAL design philosophy of the past, they also add some outstanding new features that enhance their practicality, convenience, and appeal. Quite simply, they are the lightest, stiffest, and most technologically advanced brake calipers that have ever been within the average enthusiast's grasp.
These intricate calipers have traditionally been machined from proprietary aluminum alloy billets. As one can imagine, machining away all of that material to achieve the final form is both time-consuming and costly. As a result, the price of these calipers has historically been prohibitive for the average club racer, time-trialer, or HPDE participant. Fortunately, the Pro5000R calipers use a new drop-forging technique that has dramatically lowered the manufacturing cost and the resulting price of entry, bringing this incredible technology to the masses.
Radi-CAL = Massive Dynamic Stiffness Increase
Over the years, many different strategies have been employed to shrink the brake caliper footprint while maintaining adequate stiffness: More robust caliper bridge designs, two-piece calipers with steel through-bolts, exotic materials (i.e. Beryllium, MMC), forging rather than casting, monobloc design, etc. All of these innovations pushed calipers towards becoming lighter, smaller, and stiffer. However, until the advent of the Radi-CAL, the same basic rectangular, boxy shape remained the accepted standard.
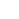
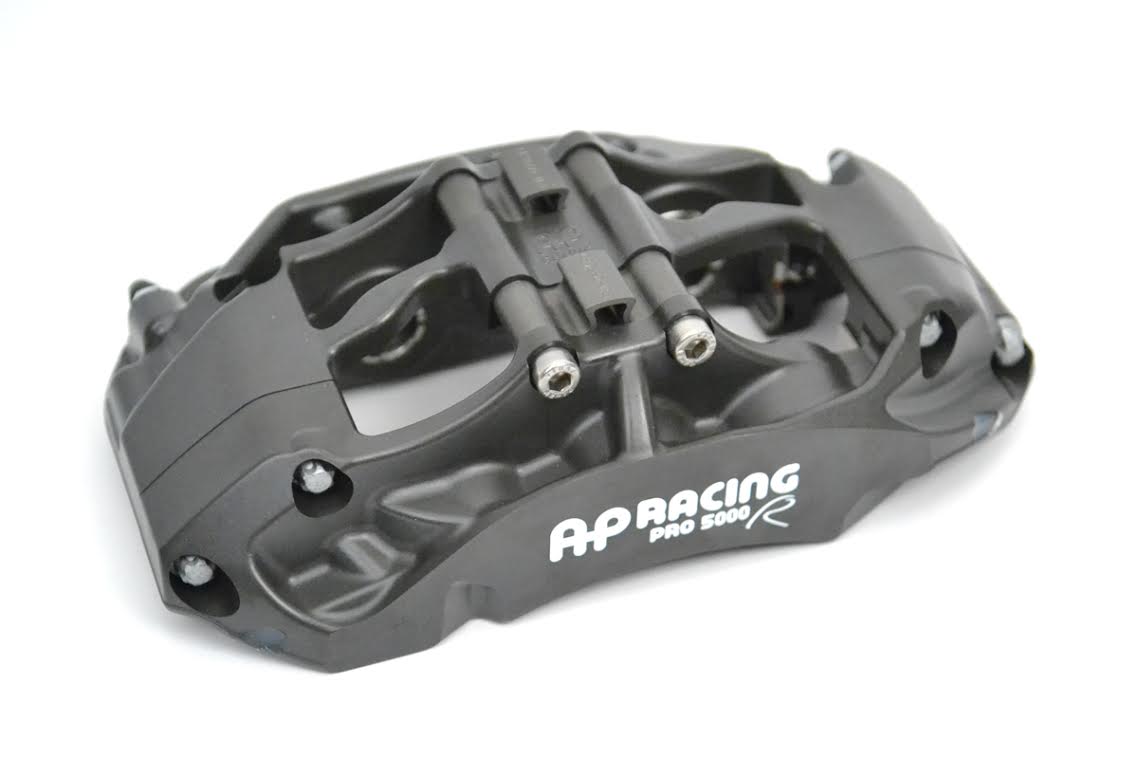
Is a rectangular box really the most appropriate and efficient shape for a brake caliper however? AP Racing has now proven that it is not. As a brake caliper clamps brake pads against a spinning disc, a tremendous tangential friction force occurs between the pads and the spinning disc. In other words, the caliper is pulled strongly in the direction of the spinning disc, as represented by the downward pointing arrow on the right side in Figure 1 below. The caliper resists that force via the spindle hard mounting points, depicted by the upward arrow on the left. The dynamic load placed on the caliper twists or pulls the caliper into a parallelogram shape.
Figure 1
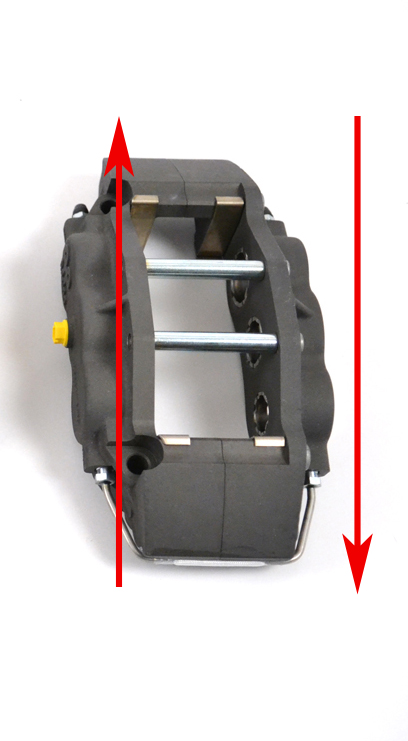
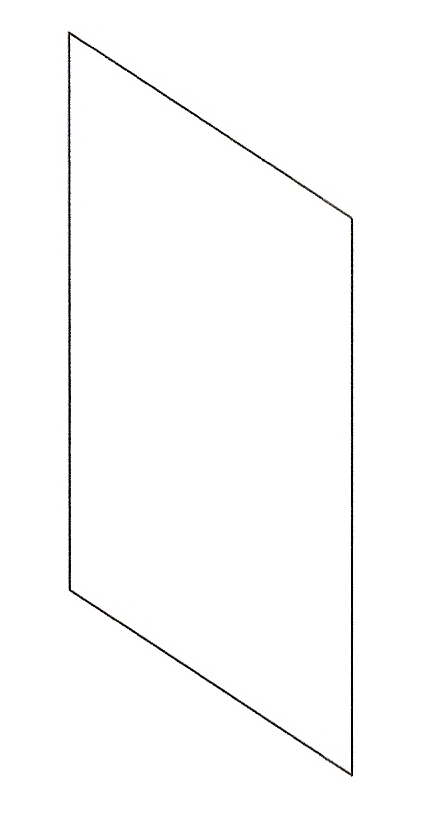
The dynamic force exerted on the calipers during a braking event is the key to the magic of the Radi-CAL design philosophy. Brake calipers of the past were designed to some extent in relative isolation from the forces that they were attempting to combat. They were designed to be the stiffest box possible while resting on a table, with much of the caliper mass residing at either end. The Radi-CAL is dramatically different because it was deliberately designed around the braking event forces that will be acting upon it. This is achieved by optimally distributing the body mass of the caliper on a diagonal, rather than at the two caliper ends. As such, the forces dynamically acting on the caliper are supported by the caliper mass, rather than what historically has been an empty box (see Figure 2 below). At the same time, this also allows for a significant reduction in overall mass, because all non-essential, non-load-bearing caliper body material is removed. So in the case of the Radi-CAL, it's not just about the material that is put into the caliper, it's about the material that is taken away!
Figure 2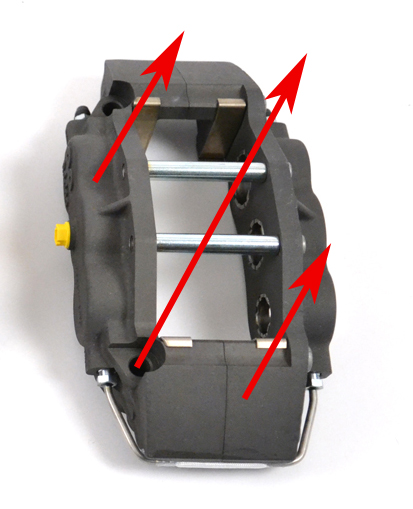
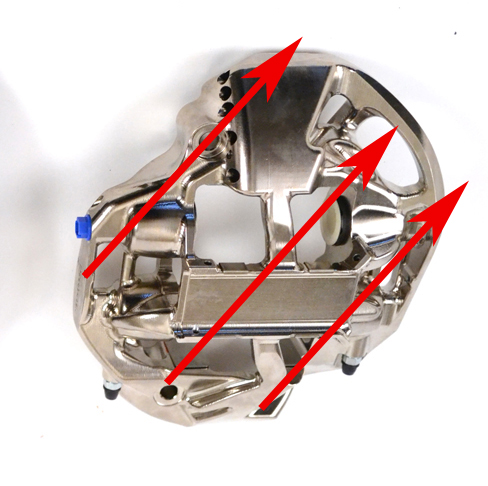

What does the above mean for you, the driver? It means a significantly firmer brake pedal with superior modulation under all conditions. It also means more even pad wear with less tapering, and a longer caliper service life.
Radi-CAL= Ultra-lightweight, Compact Design with High Airflow
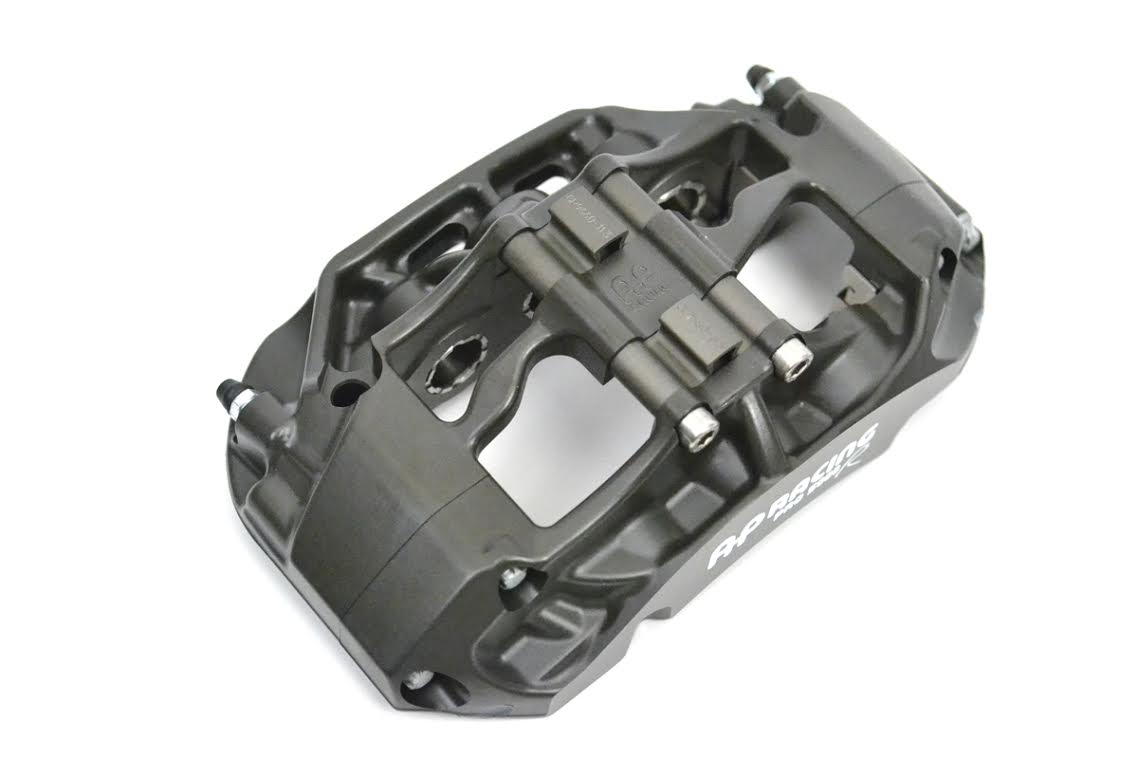

As mentioned above, the Radi-CAL design philosophy is just as much about what isn't
there, as it is about what is there. The Radi-CAL design relocates
caliper mass, creating voids that would traditionally not be located
where they are. As such, considerable mass is removed from the body,
and the entire envelope of the caliper is optimized. The result is an
extraordinarily lightweight and compact footprint.
Whereas many
competing six piston calipers weigh in the 9-12 lb. range, the CP9660
weighs an astounding 6.1 lbs.!
The Essex mantra when designing brake kits has always been, "Anything larger than necessary to get the job done is simply dead weight to drag around," and the Radi-CAL aligns perfectly with those values. One of the major problems with many of the brake packages currently on the market is wheel fitment. You’re offered gigantic discs and 12 piston calipers, with a pat on the back and a, “Good luck finding wheels to clear those things (insert sinister chuckle here).” The reality is that many casual racers want to use their OEM wheels on the track, or the smallest, lightest wheel they can find. Not only is saving unsprung weight critical, R compound tires are much more plentiful and cheaper for smaller wheels. If the components are designed properly with heavy use in mind, you don’t need to cram boat anchors under your wheels. If you’re worried about the loss of stiffness due to mass reduction, don’t. Some manufacturers use a heavier six piston caliper, but that's because the caliper wasn't designed or optimized for racing. In those cases, the same caliper may have been designed for use on much heavier road cars, and even trucks! AP Racing’s Pro5000R calipers are incredibly stiff, and designed from scratch with only the racetrack in mind.
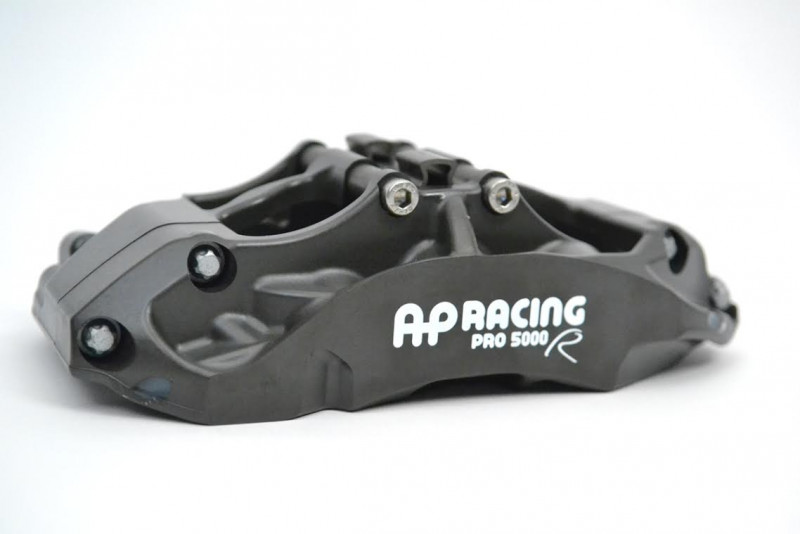
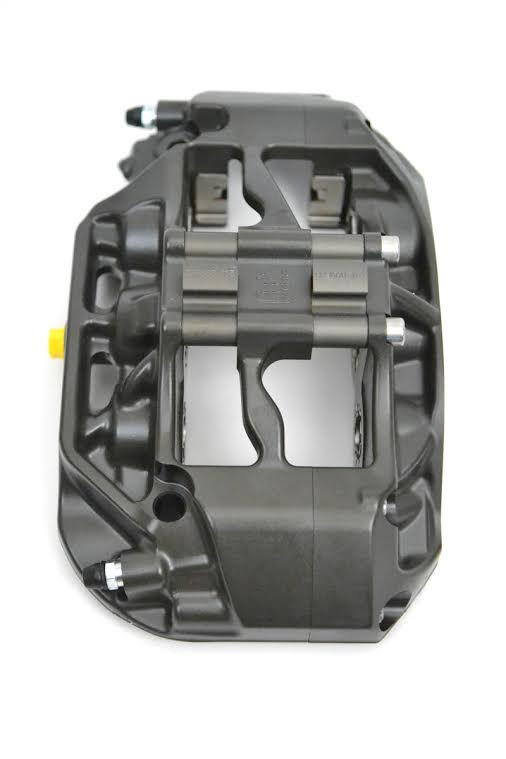
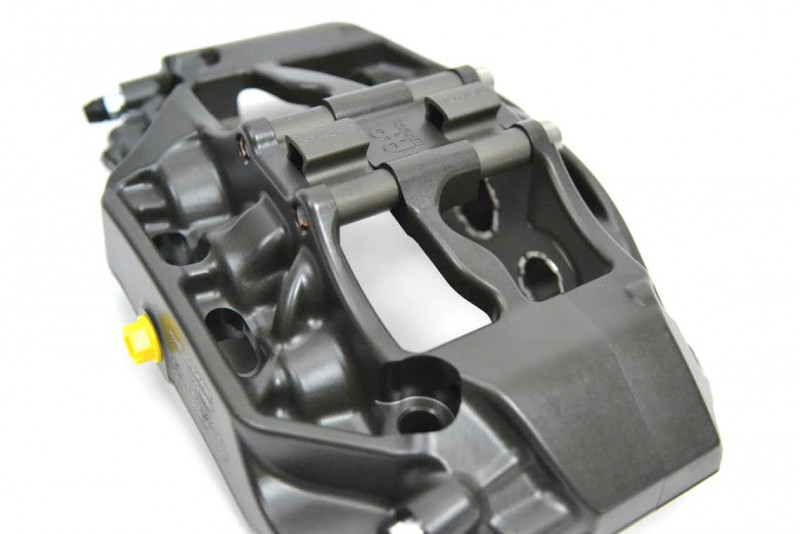
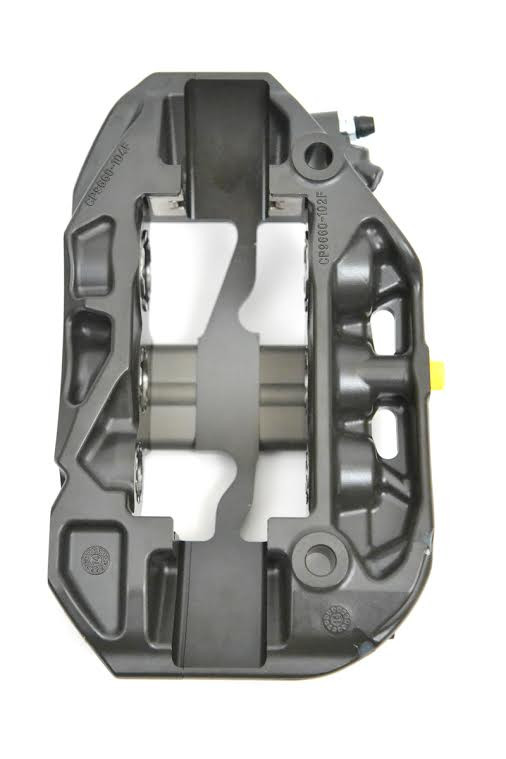
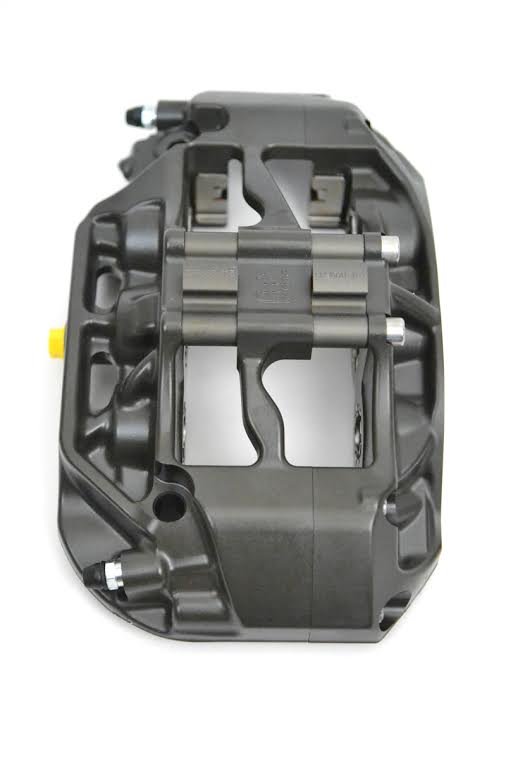
Take a look at the caliper above or below. Anything else missing? Outer bleed screws and crossover tubes! The Pro5000R range has internal fluid porting and only two bleed screws located on the inner caliper half. That means that the chance of knocking a bleed screw or denting a crossover pipe during a wheel change virtually disappears. It also means that you now have half as many bleed screws to turn when changing your brake fluid. Eliminating the piping and bleed screws also allows the outer corners to be rounded, improving wheel spoke clearance.
Finally, take a look at area around the pistons in the picture below. Compared to a traditional caliper, far more surface area around the pistons is in contact with the cooling air surrounding caliper. As a result, the calipers have more airflow through and around them, lowering their overall operating temperatures.

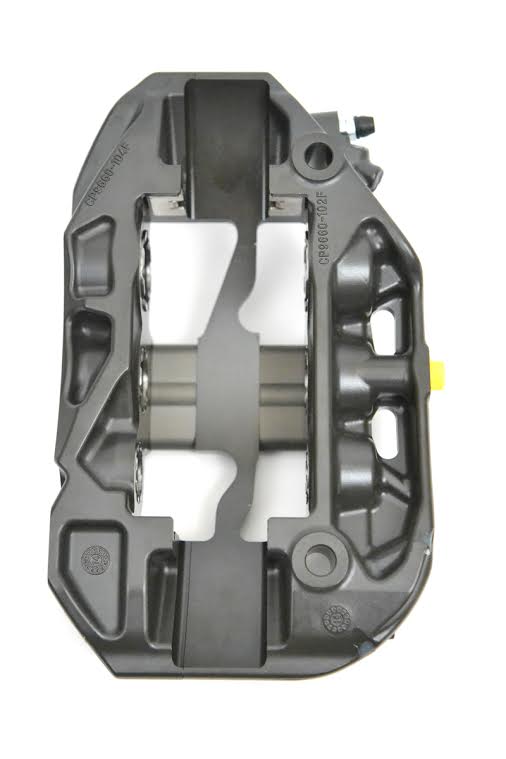
Two-piece, Drop-Forged Caliper Body
Radi-CAL's such as the one in Figure 2 above have traditionally been
machined from a single, solid block of proprietary aluminum alloy
(monobloc). With a monobloc design, the piston bores and piston seal
grooves can only be machined with a right angle machine tool (the tool
must be inserted up and into the caliper). As one can imagine,
machining away all of that material with special tools and multiple
setups to achieve the final form is both time-consuming and costly. As a
result, the price of monobloc Radi-CAL's has historically been
prohibitive for the average club racer, time-trialer, or HPDE
participant. The Pro5000R has been made possible by a newly developed
2-piece drop-forging process, which allows a conventional machine tool
to access the piston bores via a direct path. The result is a drastic
reduction in both production time and cost, while still retaining an
incredibly stiff form.

Hard Anodized Finish
The first obvious weakness when looking at a typical aftermarket caliper is the finish. Most aftermarket calipers come in a painted finish, whether they are red, black, or gold. That painted finish is designed to look pretty and prevent corrosion in harsh winter environment. Unfortunately, for all of the compliments painted calipers generate, there is an associated price if you drive the car in a track environment. That price is the chipping, flaking, fading, color shift, and general degradation of that finish in a fairly short period of time. Some OEM calipers can go from the as-delivered color to a nasty shade of brown in as little as one weekend. While this is typically worn as a badge of honor among our more hardcore customers, let’s face it…they still look terrible. More importantly however, all of those bits of paint end up in places they’re not supposed to, which we’ll get to in a minute.
Why does this happen? Heat. Paint and powder coat cannot adequately handle track temperatures. Powder coat also has some notorious issues with shrinkage. The powder coat layer expands and grows when the caliper is heated. When it cools, the powder coat doesn’t necessarily shrink in step with the caliper body itself. What’s left is a loose shell of finish hanging limply on the caliper body. That shell then cracks and falls to pieces.
Paint can also have similar issues depending on how it is applied. If you were to line up a few aftermarket calipers from the same manufacturer, you would likely see that the painted finish on each of those calipers is slightly different. Some have a thicker coat, some thinner, slightly different shades of red, etc. Painting is to some extent an art form, and must be performed in a tightly controlled environment. If it isn’t, you’re always going to see variation. A thick coat makes the part look soft around the edges, and is prone to cracking off in the same manner as the powder coat described above, leaving the underlying finish exposed. A part without enough paint will look uneven, and will not protect the underlying aluminum particularly well either. In addition to problems with cracking, flaking, and uneven application, paint and powder coat also experience extreme color shift when heated. Red becomes maroon or black, gold becomes brown, and black just gets uglier.
The calipers we are using in the Essex Radi-CAL Competition Kits are ultra-lightweight, stiff, and durable under all track conditions. The finish is a hard anodizing, which is the business under track conditions. When raw aluminum reacts with the oxygen in the air, a hard surface film develops on aluminum which prevents further degradation. The process is called oxidation, and you can think of it like rust. The anodizing process leverages this natural phenomenon, and takes it a step further to produce an extremely hard protective layer of aluminum oxide on the aluminum. It does so by running an electrical current through an acid bath, and dying it to the desired color. If you want to know more, Google it.
The result is a finish that is far more appropriate for racetrack use. Anodizing creates a uniform surface that is much more abrasion resistant than paint or powder coat. That means if you ding an anodized caliper with a box wrench when bleeding it, a big chunk of the finish isn’t going to chip off into your hand. While anodized calipers will still exhibit color shift, it will take a lot more heat to get them to change, and they won’t change as dramatically. More importantly though, you aren’t going to have bits of anodizing sticking to the sides of your pistons.

Brake Pads in A Commonly Available Shape
The basic pad shapes for the Pro5000R calipers were created by AP Racing many years ago, and are used by a wide range of racing calipers today. They're available in just about every popular racing compound on the market. That means you’ll never end up in a pinch without pads.
Below is a drawing of the basic pad shape:
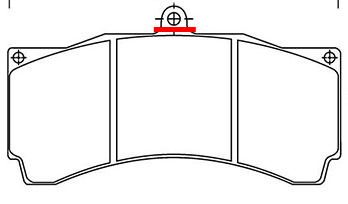
Dimensions= 152.1 x 54 x 18 mm
Pad Retention Loop
The basic pad shape above comes from some manufacturers with a small loop on the top edge (the portion above the red line in the drawing above). On certain calipers a pad retention pin is placed through that loop to hold the pads in place. That small loop is not used in the AP Racing Pro5000R Radi-CAL's however, and must be removed for the pads to fit properly. If the pads you're planning to run have that loop, you'll need to remove it from each pad before use (it can be sawed or ground off in a matter of seconds).
Pad Thickness, CP9660 caliper (18mm) vs. CP9668 caliper (25mm)
For many of the platforms we are servicing, we have both the
CP9660 and CP9668 calipers available. The biggest difference between
these two calipers is the thickness of the pads that they can
accommodate. The CP9660 caliper uses an 18mm thick pad in the above
shape, while the CP9668 caliper uses a 25mm thick pad. Which one is
right for you? If you're running multi-hour endurance races, or if you
want to reduce the frequency of pad changes, the CP9668 is likely your
proper choice. If you're running standard 20-40 minute HPDE/Time Trial
sessions, or sprint races, the 18mm thick pads will be more than ample.
There are two primary tradeoffs when going with the CP9668 caliper: It
is about a pound heavier (including the difference in pad weight), and
roughly 14mm wider than the CP9660. You will lose that 14mm on wheel
spoke clearance vs. the CP9660 kit, so please make sure to check both
fitment templates if you're debating on caliper choice.
The available pad compounds that Essex sells for the CP9660
caliper can be found below. Please keep in mind that there are many
other compounds available on the market from other manufacturers. The
list below represents only what Essex sells. When purchasing our
system, you have the option of buying one set of brake pads at 50% off
of the retail price. Underneath the manufacturer list below, the pad
compounds are listed from most aggressive to least aggressive.
CL Brakes
Ferodo Racing
Hawk Performance
Note on using brake pads different from those listed above
Again, please keep in mind that the above is not an exhaustive list, and that there are many other pad compounds available in this shape from other manufacturers. Please note however, that the pad shape we use in our caliper is available in a variety of radial depths (heights), and that Essex recommends the 54mm radial depth version. Another common radial depth in this pad shape is 51mm. The 51mm depth pads will fit into our caliper, but you will be leaving an unswept 'ring' around the disc near the attachment points to the hat (the pad will not hang as low in the caliper). Leaving a portion of the disc face unswept can create a temperature differential across the face of the disc, and doing so could lead to premature disc cracking.
Pad Cross Reference
Since
we do not sell most of the brands listed below, Essex cannot guarantee
the fitment of these pads in the AP Racing CP9660 caliper, and they may
need to be modified as shown above (loop removed). Based on our research
however, we believe that these are the appropriate cross references for
the basic shape. However, you should verify with either the
manufacturer or your installer prior
to purchasing any of them for use in the Pro5000R calipers.
| Manufacturer | Part Number | 18mm | 25mm | Depth |
| Alcon | PNF4489X532.4 | X | X | 52 |
| AP Racing | CP3894D54 | X | X | 54 |
| Brembo | B51 | X | X | 54 |
| Carbotech | CTP7790A | X | ? | 54 |
| Circo | MB1658-25 | X | X | 54 |
| CL | CL5009 | X | X | 54 |
| Cobalt | AP5 | X | X | 51 |
| EBC | (DP2006, DP3006C, DP4006) | X | ? | 54 |
| Endless | RCP086 (D52) | X | X | 52 |
| Ferodo | FRP3003 | X | X | 54 |
| Hawk | HB109 | X | X | 54 |
| Mintex | 1852 | X | X | 51 |
| Pagid | U1903 | X | X | 54 |
| PFC | 7790.XX.18 | X | X | 54 |
| Porterfield | AP7790 | X | X | 54 |
| Project Mu | F1090 (D52.5) | X | X | 54 |
| Raybestos | R2600 | X | X | 54 |
| Wilwood | 8825 | X | X | 51 |
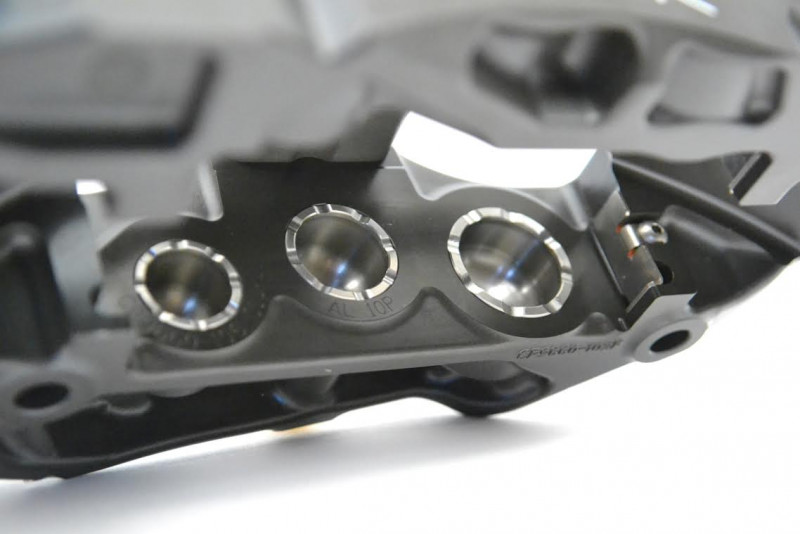
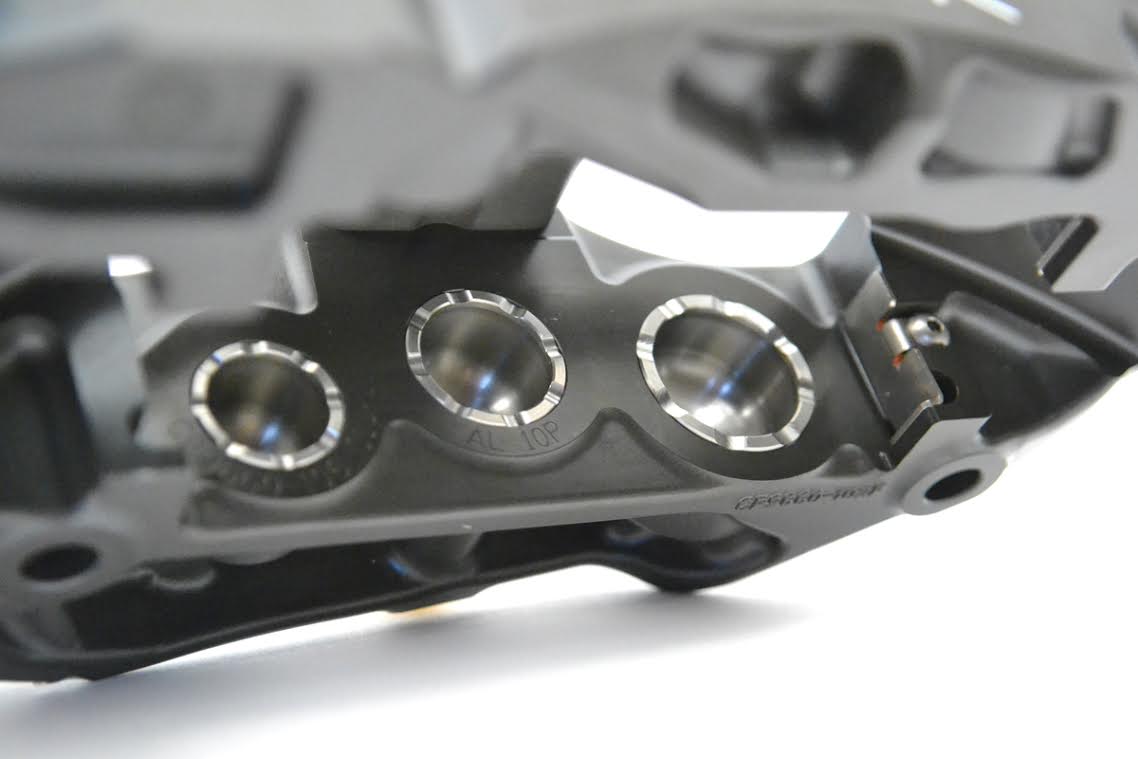
Ventilated, Domed Back, Stainless Steel Pistons
There are people who will tell you that aluminum pistons are great for track calipers. They will tell you that the expansion rates of the pistons and caliper body need to be the same when heated. This argument is completely invalid and unproven. Those same people tend to get upset when you point out the fact that every serious race caliper, from every serious race caliper manufacturer on the planet uses either stainless steel or titanium pistons, period. There is a reason for this: they're better!
Stainless steel pistons are far superior to aluminum pistons in creating a thermal barrier. They are much better at keeping heat out of your brake fluid and preventing a soft pedal from fluid fade on the track. This has been proven over and over again at all levels of motorsport. While most aftermarket calipers use a pressed aluminum piston, the Pro5000R's use an expensive machined stainless steel piston.
To add stiffness to the pistons, AP designed the back of the piston with a domed back. At first glance this seems like a trivial design element. It is not. When domed back pistons were introduced in professional racing, driver feedback was immediate and resoundingly positive. The domed back adds considerable stiffness that can be felt through the pedal, and they have now become the standard vs. which all designs are judged.
For even greater heat resistance, there is ventilation on each piston. The air gaps around the piston edge allow for even more cooling air circulation around the pistons. All of these features slow and repel the influx of heat into the brake fluid, preventing brake fluid boiling and fade
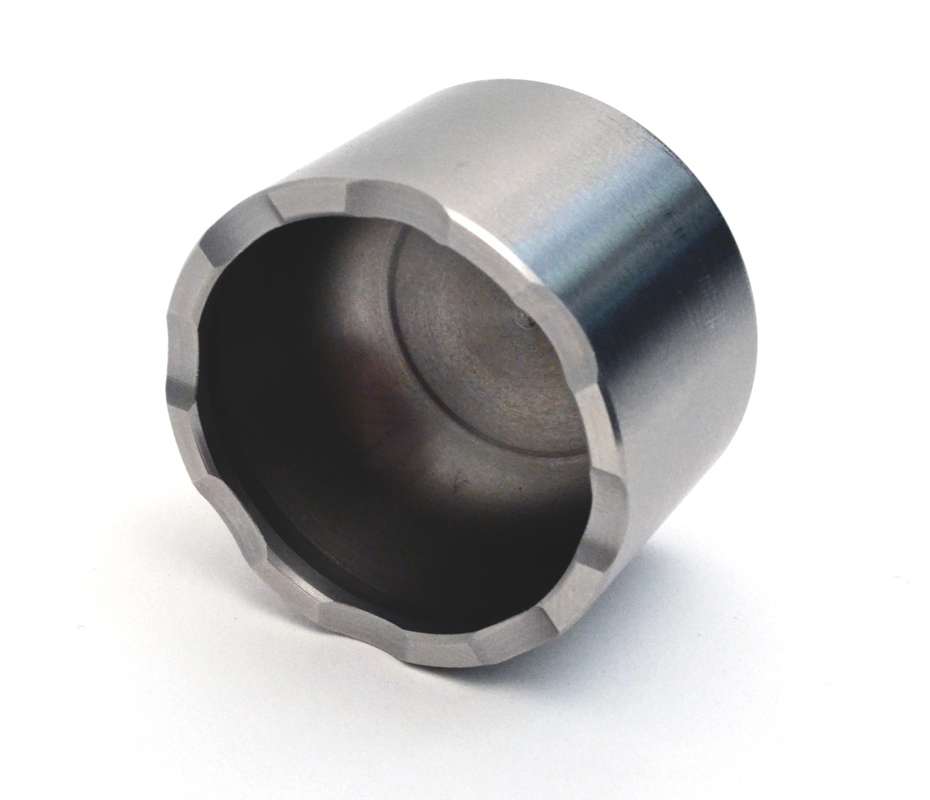


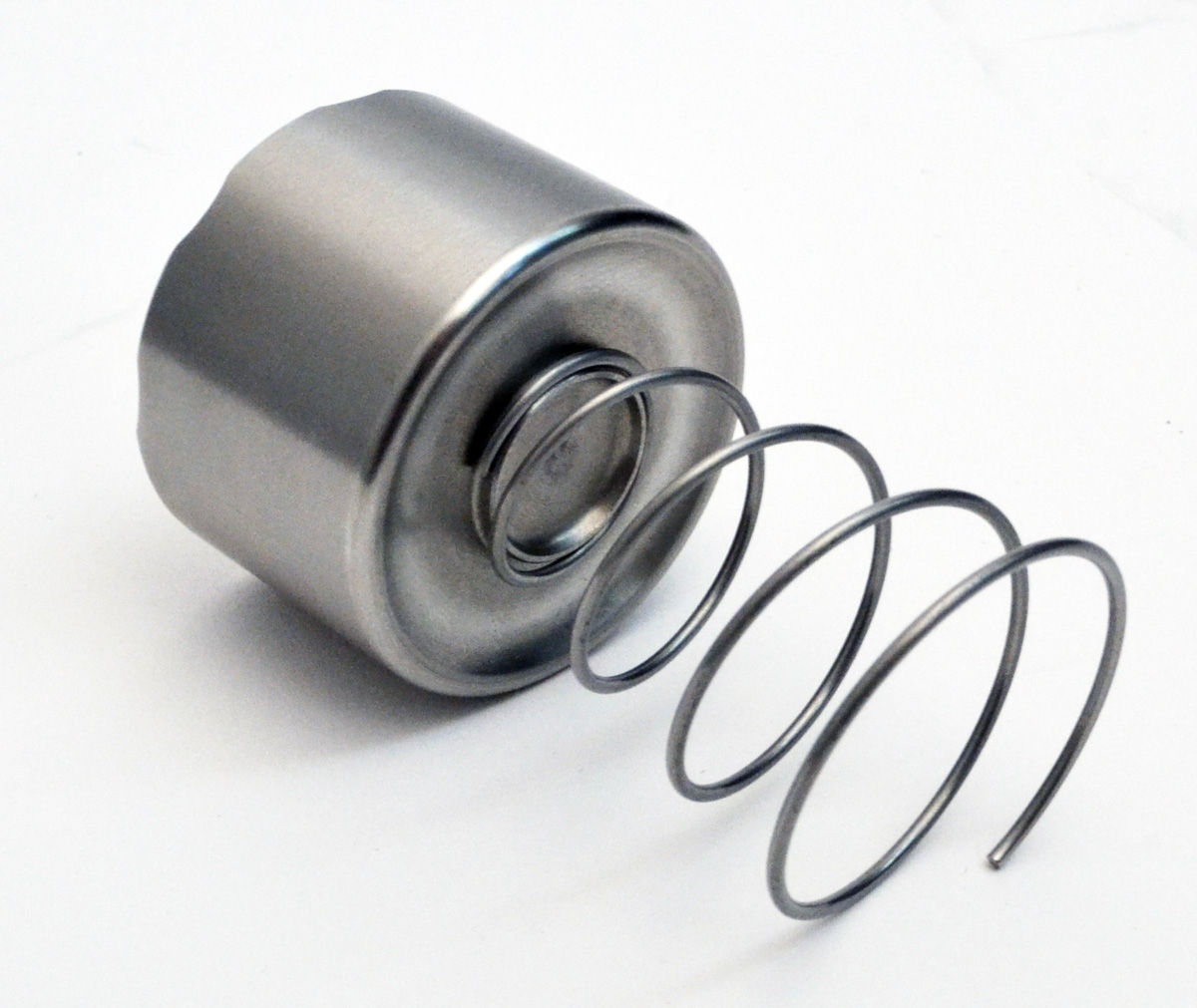
Anti-knockback Springs
Not only are the pistons stainless steel, they are fitted with anti-knockback springs. Springs in pistons you ask? Yes, springs. If you’ve ever gone through a series of S turns and then had your pedal drop when going into the following brake zone, you have experienced knockback. To say it is disconcerting is an understatement. You’ll often see pro drivers ‘pre-tap’ their brakes lightly when approaching a brake zone. They are fighting knockback.
Knockback is a phenomenon that is common with fixed calipers. Knockback occurs when your car’s wheel, hub, and bearings deflect during cornering, allowing your brake disc to move out of sync with your caliper and brake pads. The amount of knockback varies by vehicle, and depends on the amount of deflection seen in the parts listed above. As the brake disc deflects, it actually pushes the pads away from each other, forcing the caliper pistons back into their bores. The piston seals don’t have enough tension in them to completely return the pistons to their original location. That means there is slack in the system that needs to be taken up. When you press the brake pedal, it will continue to drop until that slack is taken up.
Anti-knockback springs help alleviate this situation by putting some tension on the back side of the pistons. When the disc deflects and makes contact with the pistons, the springs push the pistons back into their proper location, reducing slack in the system. That means less pedal drop and far fewer pucker-factor moments when going into heavy brake zones.
There are no major downsides to lightweight AKB spring as long as the caliper is designed to accommodate them. More specifically, AKB springs do not create any increased drag or wear on the pads and discs as long as the shape and material of the piston seals takes them into account.
As you're driving the suspension is constantly compressing, the disc is moving around laterally, and the pads are being pushed slightly away from the disc. Think of the seals in the caliper as a spring or hinge attached to the side of the piston, rather than just a ring through which the piston slides. In an AP Racing competition caliper, the groove in which the seal resides isn't a square cut groove.It has angles. When the pistons slide in or out there is friction between the outer piston wall and the seal, and the seal distorts a bit as shown in the illustration below.
A caliper piston sliding out to the left woulddistort the seal in this manner (the slashes are the seals on either
side of the piston):
/
---
---
\
As the piston slides back in to the right, the seal does this:
\
---
---
/
There is a certain amount of tension or friction that needs to be
overcome before the piston actually starts moving through the seal ring.
That tension/friction keeps the piston from dragging on the disc once
the pistons are pushed back into the bores by the disc/suspension
movement.
When AKB springs are added, a little more force is
required to push the pistons back into their bores than would be
required without them.After the spring is compressed, it unloads and
pushes the piston back to 'neutral.'
With the proper seal and
spring the goal is to keep the piston in the 'neutral' position, not
pressed against the disc.The piston is still able to slide freely in
either direction, but a bit of friction or tension needs to be overcome
initially to get it moving in either direction. The seal offers that
first bit of friction to limit movement, and then the spring provides
additional resistance. The end result is that the properly designed AP
Racing calipers won't drag or create additional or unnecessary wear.
High Temperature, Low Drag Seals Without Dust Boots
We are often asked by potential customers if the calipers in our kits require frequent maintenance and rebuilding because the pistons don't have dust boots. We are perpetually shocked by this question because it makes no intuitive sense. If you have a product that is specifically designed to handle the extraordinary high-heat conditions of track use, why would it require more maintenance when used under those conditions vs. brake components that were designed to cruise around on the streets at low speed and temperature?
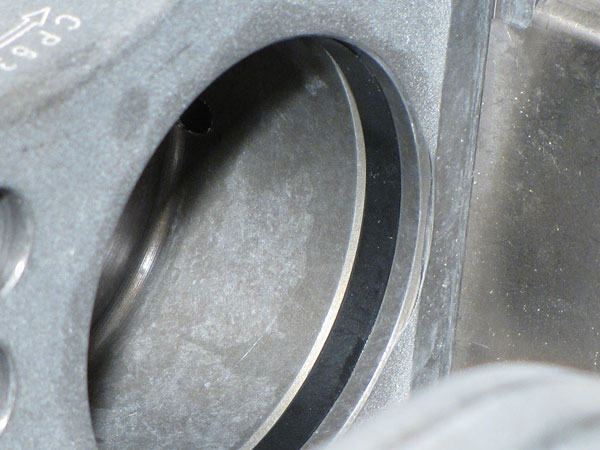
Many people confuse piston seals with dust boots. All calipers have seals. They're the little rubbery rings inside the piston bores (see pic below). If a caliper didn't have a seal, your brake fluid would leak out around the pistons! OEM caliper seals aren’t designed to handle constant trips to several hundred degrees without becoming brittle and leaking. Our calipers use special high-temp seals designed for track use. They are the exact same high temperature seals used in NASCAR Sprint Cup, ALMS, DTM, etc. That means they are less likely to get brittle and wear out when used under high-heat track conditions, and they require far LESS frequent replacement and servicing.
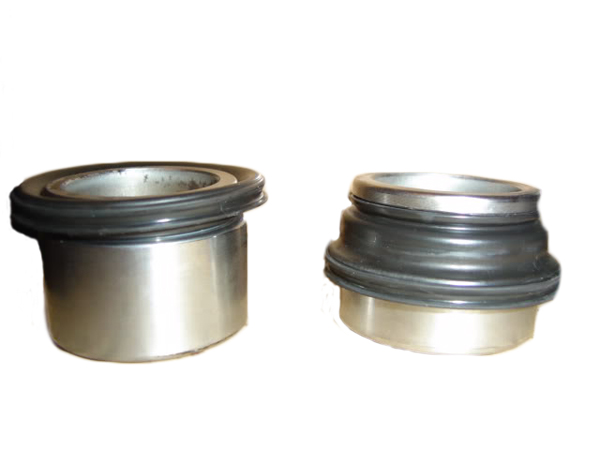
Most aftermarket calipers are designed for year round road use, and as such come with a bellows style external dust boot like the ones shown below. The rubber boot stretches as the piston extends, and its objective is to keep contaminants out of the piston bore. It's a nice concept, but we've seen customers burn those up in a single 20 minute track session! Once that happens, you're simply driving around with some tattered, burnt rubber bits attached to your pistons. At that point they're providing zero benefits to you. If you're going to instantly destroy them when you go to the track, why worry about having them in the first place? We skip making that mess for you by eliminating them from our design.
AP Racing High-Temp Piston Seal

OEM Dust Boot Before Track Use


Simple Pad Change with Two Bolts
After the countless times you’ve changed your brake pads, you’re
probably never too excited when it comes time to do so. Changing pads
will no longer be a chore with the Pro5000R's. No more fiddling with a
hammer, punch, or pliers. AP’s bridge bolts pop out easily with a 5mm
hex wrench and a 7mm socket. It will take you longer to pull off the
wheel than it will to change pads. Less time futzing around in the
paddock, and more time driving= fun.

Pistons Sized Specifically for Your Car
The piston sizes in our systems are specifically chosen to closely mimic the OEM brake torque on a given axle. As such, our front systems can be bolted to otherwise stock cars with no ill-effects, negative impact on ABS, etc. The vehicles stock master cylinder can remain, as can the OEM rear brake system.
Lifetime Professional Reconditioning Service


Essex is AP Racing's official North American caliper reconditioning center. We have skilled service technicians rebuilding hundreds of AP Racing calipers each year for the top teams in NASCAR Sprint Cup, ALMS, etc. As an Essex customer, our rebuild service will always be available to you when your calipers need servicing. You simply remove your calipers from the car, drain/clean them, and ship them back to Essex. We take it from there:
Hardness testing: After disassembly your calipers will be Rockwell hardness tested against the standard for that particular caliper type as sold new. This test provides a relative understanding of how much fatigue and stiffness loss your calipers have experienced. Tired calipers lead to pad tapering, increased pad wear, leaky seals, and a loss of pedal firmness, all things you want to avoid. Essex will make a replace or rebuild recommendation based on the results of this test.
Ultrasonic cleaning: After passing the hardness test, your calipers will be placed in an ultrasonic cleaner to remove all dirt, debris, brake fluid, etc. This method produces results that are far superior to what the average racer could accomplish via hand-cleaning.
Inspection and re-assembly: All serviceable parts of the caliper will be inspected and replaced if necessary, including the seals, abutment plates, pistons, and bleed screws.
Cyclical Pressure Testing: After your calipers have been rebuilt, they will be cycled at high and low pressure on a pressure bench to ensure proper functioning. This is important, as certain leaks only show up under specific pressure conditions.
Price: The labor price to rebuild a Pro5000R is roughly $80 per caliper. That does not include parts. Assuming there has been no damage to the caliper, Essex typically recommends replacing the seals ($60) and bleed screws ($15) during the standard reconditioning process. For roughly $160, you can have a fresh, professionally serviced caliper in peak operating condition. You won't get messy, and you'll know the rebuild was done by the same folks trusted by elite-level race teams.
|
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS |
|
|
Piston Sizes - mm |
- Ø27.0 x 2 |
|
Piston Area - cm² |
50.1 |
|
Disc Diameter - mm |
- Max = 380.0mm |
|
Disc Thickness - mm |
- Max = 36.0 |
|
Weight - No Pads = Lbs. |
6.2 |
|
Hydraulic Threads |
M10x1.0 |
|
Mounting Type |
Radial |
|
Mounting Centres - mm |
180.0 |
|
Mounting Offset - mm |
42.0 |
|
Mounting Hole Ø - mm |
12.15 Nominal |
|
PL Dimension - mm |
63.5 |
|
Bleed screw Tightening Torque - Nm |
17 |
|
SPARE PARTS |
|
|
Pistons |
- Ø27.0 = CP9660-114 |
|
Seal Repair Kit |
CP8518-CEJ |
|
Anti-Knockback Spring |
CP6518-4LBSSL |
|
Pad Retainer |
CP9660-113 x 2 |
|
Pad Retainer Bolt |
CP3796-112ST |
|
Wear Plate |
- RH = CP9660-110 |
|
Bleed screw Kit |
CP3880-1 |
Brake Pads
The basic pad shapes for the Pro5000R calipers were created by AP Racing many years ago, and are used by a wide range of racing calipers today. They're available in just about every popular racing compound on the market. That means you’ll never end up in a pinch without pads.
Below is a drawing of the basic pad shape:

Dimensions= 152.1 x 54 x 18 mm
Pad Retention Loop
The basic pad shape above comes from some manufacturers with a small loop on the top edge (the portion above the red line in the drawing above). On certain calipers a pad retention pin is placed through that loop to hold the pads in place. That small loop is not used in the AP Racing Pro5000R Radi-CAL's however, and must be removed for the pads to fit properly. If the pads you're planning to run have that loop, you'll need to remove it from each pad before use (it can be sawed or ground off in a matter of seconds).
Pad Thickness, CP9660 caliper (18mm)
The available pad compounds that Essex sells for the CP9660
caliper can be found below. Please keep in mind that there are many
other compounds available on the market from other manufacturers. The
list below represents only what Essex sells. When purchasing our
system, you have the option of buying one set of brake pads at 50% off
of the retail price. Underneath the manufacturer list below, the pad
compounds are listed from most aggressive to least aggressive.
CL Brakes
Ferodo Racing
Hawk Performance
Note on using brake pads different from those listed above
Again, please keep in mind that the above is not an exhaustive list, and that there are many other pad compounds available in this shape from other manufacturers. Please note however, that the pad shape we use in our caliper is available in a variety of radial depths (heights), and that Essex recommends the 54mm radial depth version. Another common radial depth in this pad shape is 51mm. The 51mm depth pads will fit into our caliper, but you will be leaving an unswept 'ring' around the disc near the attachment points to the hat (the pad will not hang as low in the caliper). Leaving a portion of the disc face unswept can create a temperature differential across the face of the disc, and doing so could lead to premature disc cracking.
Pad Cross Reference
Since
we do not sell most of the brands listed below, Essex cannot guarantee
the fitment of these pads in the AP Racing CP9660 caliper, and they may
need to be modified as shown above (loop removed). Based on our research
however, we believe that these are the appropriate cross references for
the basic shape. However, you should verify with either the
manufacturer or your installer prior
to purchasing any of them for use in the Pro5000R calipers.
| Manufacturer | Part Number | 18mm | 25mm | Depth |
| Alcon | PNF4489X532.4 | X | X | 52 |
| AP Racing | CP3894D54 | X | X | 54 |
| Brembo | B51 | X | X | 54 |
| Carbotech | CTP7790A | X | ? | 54 |
| Circo | MB1658-25 | X | X | 54 |
| CL | CL5009 | X | X | 54 |
| Cobalt | AP5 | X | X | 51 |
| EBC | (DP2006, DP3006C, DP4006) | X | ? | 54 |
| Endless | RCP086 (D52) | X | X | 52 |
| Ferodo | FRP3003 | X | X | 54 |
| Hawk | HB109 | X | X | 54 |
| Mintex | 1852 | X | X | 51 |
| Pagid | U1903 | X | X | 54 |
| PFC | 7790.XX.18 | X | X | 54 |
| Porterfield | AP7790 | X | X | 54 |
| Project Mu | F1090 (D52.5) | X | X | 54 |
| Raybestos | R2600 | X | X | 54 |
| Wilwood | 8825 | X | X | 51 |